EU’s position in the global AI landscape
As global competition in artificial intelligence intensifies, the European Union is stepping up its efforts with renewed strategic ambition and increasing funding.
According to the 2025 AI Index Report from Stanford University, the top 15 countries from North America, Europe and Asia invested a total of $144.72 billion in AI. Of this, six European nations, which include Sweden, France, Germany, Austria, the Netherlands, and Italy, contributed $12.39 billion, resulting in a 111.79% increase compared to the previous year.
Despite this progress, the EU still faces significant challenges such as fragmented initiatives, regulatory complexity, global competition, and a widening skills gap. Without coordinated, bold action, Europe risks falling behind in the race for ethical and impactful AI leadership.
To secure its digital future, the EU must continue investing strategically, not just to boost innovation and competitiveness, but to ensure AI aligns with European values like ethics, privacy, and human rights. Open source can be a key differentiator, enabling transparency and collaboration across borders.
Europe is addressing this with huge investments in research programmes
The EU is responding to AI challenges through strategic investments in research programmes and clear policy direction through initiatives like Horizon Europe, Digital Europe, and AI-Data-Robotics Partnerships. These efforts aim to bridge the skills gap, support cross-border collaboration, and develop AI solutions that reflect European values.
The EU’s focus on regulatory frameworks like the AI Act creates a trustworthy environment, encouraging AI adoption while safeguarding privacy and human rights. This ensures Europe remains competitive on the global stage, while keeping innovation aligned with its ethical standards.
As the EU continues toward digital sovereignty in AI, open source has emerged as a powerful tool for transparency, innovation, and global competitiveness. The European open source community is gaining momentum, with more visibility and engagement on GitHub.
However, in recent times, it has been noted that AI technologies often withhold critical components such as training code, even when model weights are shared. According to 2025 AI Index Report, over 60% of notable AI models were released without accompanying training code in 2024, signalling a shift away from full transparency.
In this context, the Eclipse Foundation plays a vital role in ensuring EU-funded AI research remains open, transparent, and aligns with the EU’s digital sovereignty goals and emerging legal frameworks such as the AI Act and open science policies.
Eclipse Foundation involvement in research - what we are doing
Since 2013, the Eclipse Foundation has participated in over 30 research projects in collaboration with over 730 partners, with 15 active projects currently underway across key technology domains including security, cloud, data spaces, software-defined vehicles, embedded, IoT, open hardware, and AI. Among these, Eclipse Foundation is making a direct contribution to the advancement of AI through projects such as Eclipse Aidge, Eclipse LMOS, Eclipse GRAPHENE, or Eclipse Theia AI, exemplifying our commitment to fostering a strong, open source culture in AI.
Our mission is to support research consortia in transforming their research outcomes into thriving open source projects. We focus on community building and active engagement with the Eclipse open source ecosystem to maximise impact. We provide guidance on open collaboration best practices and offer support for intellectual property and license management, ensuring research results lead to valuable, exploitable open source software. We believe this is a key factor for successful technology transfer from research to industry.
This is especially critical in the field of AI, where open source plays a key role in addressing many of the challenges Europe faces. Building sustainable open source projects and thriving communities from the European Research ecosystem is key to a successful European AI future.
The Eclipse Foundation is currently participating in a range of Horizon Europe projects that address these key challenges. These include:
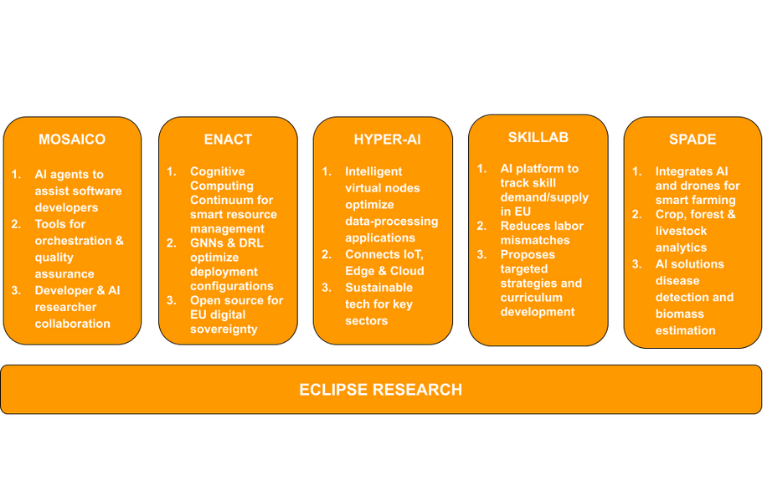
MOSAICO aims to revolutionise software development by establishing a collaborative ecosystem where AI agents seamlessly work alongside developers to boost efficiency, improve software quality, and strengthen the competitiveness of European software development.
This will be achieved through the development and demonstration of a comprehensive set of AI-powered tools integrated into a MOSAICO platform, supporting the entire software development lifecycle with features for communication, orchestration, governance, quality assessment, benchmarking, and AI agent reuse.
By building a dynamic community of developers and AI researchers, MOSAICO fosters conditions for widespread adoption of AI-driven software development practices.
The ENACT project advances AI in distributed computing, building a Cognitive Computing Continuum for smart resource management and dynamic scalability from edge to cloud.
Using Graph Neural Networks and Deep Reinforcement Learning, ENACT creates an intelligent decision-making engine that suggests optimal deployment configurations for hyper-distributed applications based on their specific needs, replacing scheduling components in open source platforms like KubeEdge. These innovations enhance the adaptability and efficiency of computing infrastructures, particularly in data-intensive and latency-sensitive scenarios.
As a member of the EUCloudEdgeIoT community's cluster, ENACT supports Europe’s digital sovereignty with open source solutions, strengthening leadership in AI, data, and robotics, and aligning with its goals for technological independence and sustainable digital growth.
The HYPER-AI project seeks to advance distributed computing by addressing the challenges of integrating Internet of Things (IoT), Edge, and Cloud computing environments. Its primary focus is on developing intelligent virtual computing nodes that can optimise data-processing applications across distributed networks to improve performance and efficiency.
The project utilises autonomous, self-organising computing swarms to enable flexible connectivity and collaboration among diverse computing resources. This facilitates smoother integration across the computing continuum—from edge devices to cloud infrastructure—through the use of semantic representation and orchestration methods.
HYPER-AI aims to support adaptable and efficient computing ecosystems capable of handling complex applications in areas such as healthcare and energy, contributing to the ongoing development of digital technologies and sustainability efforts.
The SKILLAB project aims to develop a comprehensive platform for skills management and shortage identification. It will monitor the demand for specific skillsets among European organisations, the supply from job seekers and potential employees, and relevant European policies. Based on this data, the platform will propose targeted strategies, curriculum development, policy recommendations, and job advancement opportunities.
At its core, SKILLAB leverages Artificial Intelligence to analyse vast amounts of data from the labour market, organisations, and European taxonomies and initiatives. This AI-driven approach will help reduce labour shortages and mismatches across regions, sectors, and timeframes.
The SPADE project focuses on integrating artificial intelligence (AI) with unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to transform agriculture, forestry, and livestock management. By developing an open source ecosystem, SPADE leverages AI and machine learning technologies to enable advanced disease detection, point-cloud segmentation for terrain and vegetation mapping, and real-time livestock monitoring.
SPADE's mission centres on using AI to analyse drone-collected data, delivering insights that promote healthier crops, better forest conservation, and improved animal welfare. The project fosters innovation through open calls, inviting researchers and startups to develop AI solutions for challenges like disease detection and biomass estimation. By combining AI with drone technology, SPADE is driving a new era of precision agriculture and environmental stewardship across Europe's rural landscapes.
As Europe redefines its digital future, the Eclipse Foundation remains committed to helping research projects succeed through open collaboration, best practices, transparent governance, and community empowerment. To stay updated on our activities, visit our website.




