In a world where software is everywhere, open source plays a vital role. Organizations looking to achieve successful digital transformation will need to leverage open source software and, increasingly, contribute to it.
To fully understand the role open source software plays in digital transformation, it’s important to consider the rise of software and the role that open source software and ecosystems play in bringing the value and benefits of software to more people globally.
Open Source Delivers Broader Benefits Than Proprietary Software
Today, software is silently taking over the world. It’s the beating heart of the phone in your pocket. It’s monitoring the quality of the water you drink. It keeps you safe on the road. These advances are welcome evolutions. Yesterday’s tools and appliances were built for a single purpose and could not be adapted to meet modern requirements. In contrast, we can add bug fixes, enhancements, and entirely new features to software-driven solutions. This change is a direct result of digital transformation.
However, it’s essential to keep in mind that not all software is the same.
Proprietary software is built behind closed doors with limited interactions with the outside world. It’s usually linked to walled ecosystems that are controlled by a single vendor or a very small group of vendors. These ecosystems concentrate decision-making power into the hands of a select few and funnel profits to them.
Open source software, on the other hand, breeds open ecosystems. These ecosystems are the only ones that deliver value to all parties involved.
Consider how bread became a staple food. We don’t know how it was first created, but it can be made from several kinds of grains, and baked in many different ways. This diversity is what makes bread great. Wherever you go in the world, you will find bread.
The reason this happened is simple: The secrets of breadmaking spread freely throughout the world. They became, in a way, open source. It’s safe to assume the world market for bread would be much less innovative and valuable if breadmaking had been controlled by only a select few.
When you apply these benefits to digital transformation initiatives, it’s easy to see why open source has become so prevalent. IoT is a particularly good example.
The IoT Industry Relies Heavily on Open Source
In the 2021 IoT and Edge Commercial Adoption Survey, 74 percent of respondents stated they’re factoring open source into deployment plans. This data is supported by third-party market research as well. For example, a recent study led by the non-profit organization, OpenUK, found that 97 percent of UK businesses are using some form of open source software, operating systems, and programming languages.
So, why is open source usage so widespread in the IoT industry? In our survey, we asked respondents to identify the top reason they leverage open source technologies (Figure 1).
Figure 1: The Greatest Benefits of Using Open Source Software
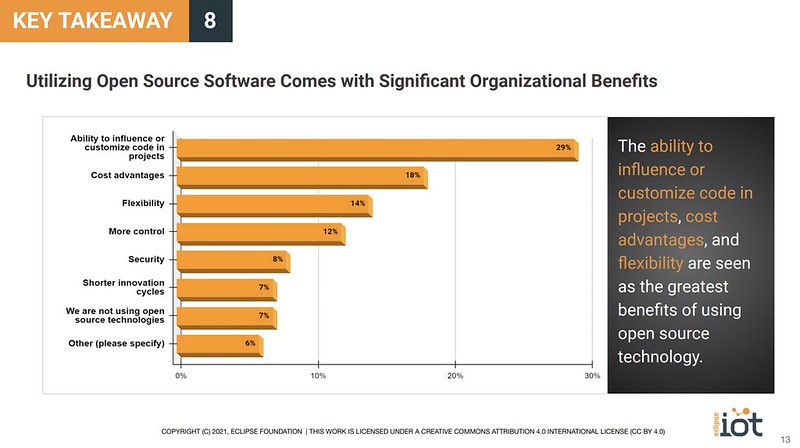
Open source software is available for free. However, this cost advantage was only selected by 18 percent of respondents. The top answer, chosen by 29 percent of respondents, was the ability to influence or customize the code. In addition, flexibility was mentioned by 14 percent of respondents.
These results can be explained by the requirements of IoT projects: They often rely on devices with limited processing and storage capabilities, and they require developers to optimize power consumption for battery-powered devices. Open source makes it easier to customize the hardware and software aspects of field-deployed devices.
If we turn our attention to two industries that rely heavily on IoT — industrial automation and automotive — we can see additional ways open source drives digital transformation.
Open Source Enables the Machine Economy in Industrial Automation
In the world of industrial automation, digital transformation means transitioning from analog to digital technologies.
The digital factory of today is very different from its analog predecessor. It’s connected to the rest of the organization through secure channels. Operational and information technology teams both shape the technology. Data is reported in real time. And the technology environment relies on open source, which leads to increased diversity among the organization’s suppliers. Finally, software-driven equipment brings previously unheard-of flexibility.
Overall, the move to digital technology in industrial automation has created optimal conditions for the emergence of a machine economy where smart machines and smart services will lead to smart value creation. This economy should, and will be, based on open source technologies and open standards.
The success of the Sparkplug specification is a good example of this evolution. The MQTT publish/subscribe protocol has been a mainstay of industrial automation for the last 20 years. However, traditional MQTT-based infrastructure and devices could not interoperate out-of-the-box because the MQTT specification didn’t define message payloads and topic structures. By defining those aspects in a generic, yet extensible way, the Sparkplug specification is now a powerful enabler for digital transformation in industrial automation.
Open Source Cuts Costs and Risks for Automotive Industry Players
Digital transformation in the automotive industry is also rooted in open source.
Vehicles have become increasingly complex, even if you don’t consider autonomous vehicles. For car manufacturers and their suppliers, developing specialized components on their own is fraught with risk. As a result, many of these organizations have entered into targeted, strategic partnerships that allow them to build the required technologies together.
Digital transformation will have a long-lasting impact on multiple aspects of the automotive industry (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Digital Transformation Opportunities in the Automotive Industry
Ultimately, a majority of the most impactful use cases will be enabled through open collaboration. In today’s environment, this is a synonym for open source.
We’re seeing this shift at the Eclipse Foundation today. Competitors in the automotive industry are pooling resources to solve complex problems that are too expensive to solve on their own. And players from the larger IT ecosystem are building IoT platforms to complement the efforts of car makers and their partners.
For example:
- The OpenMobility Working Group is developing mobility modelling and traffic simulation technologies for testing autonomous driving functions, developing new mobility solutions, and creating digital twins of urban areas.
- The Eclipse sim@openPASS project, which is fostered by the openPASS Working Group, provides a software platform for simulating traffic scenarios to predict the real-world effectiveness of advanced driver assistance systems on automated driving functions.
- The OpenADx Working Group aims to deliver an industry-accepted definition and reference architecture for the autonomous driving toolchain to improve interoperability and functionality of established development tools
- The members of the Eclipse IoT Working Group are collaborating on a growing collection of IoT building blocks that can be used to create platforms for a wide variety of industries.
With open collaboration, working groups members can define joint roadmaps and build core capabilities, sharing risks and benefits. This frees them to innovate at the top of the stack and gain meaningful differentiation for their commercial offerings.
Learn More
For more information about the advantages of the open source ecosystems hosted at the Eclipse Foundation, explore our working group benefits and members.


